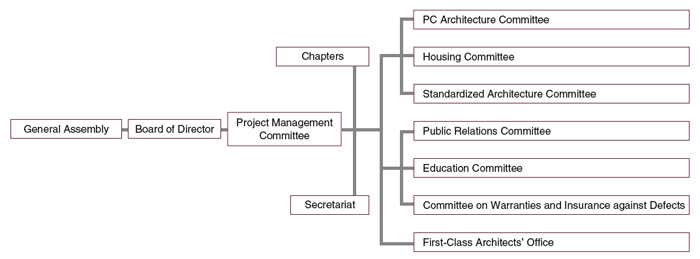
Our association was founded in January 1963 as an organization playing a central role in developing the industrial production of housing and promoting the modernization and rationalization of the construction industry.
In January of the next year, under the joint jurisdiction of Japan’s Ministry of Construction (currently the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) and the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (currently the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry), we became an incorporated association.
Further, in October 2013, we got a new start as a general incorporated association that aims to promote the creation of a rich living environment and high quality social capital through research and development on prefab architecture as well as its construction and propagation.



The PC Architecture Committee focuses on architecture using precast reinforced concrete (PC) components as the main structural member (PC architecture).

The PC Architecture Committee focuses on architecture using precast reinforced concrete (PC) components as the main structural member (PC architecture). The construction methods involved have diverged into many branches but the main methods being used presently are ① the wall-precast reinforced concrete (W-PC) construction method, ② the framed wall precast reinforced concrete (WR-PC) construction method, ③ the rigid-frame precast reinforced concrete (R-PC) construction method, and ④ the precast reinforced concrete encased steel frame (SR-PC) construction method.
These can be used for all kinds of concrete buildings, beginning of course with multiple-dwelling housing complexes, and including office buildings, shops, warehouses, medical facilities, sports facilities, etc.
The PC Architecture Committee promotes development of technology for designing PC buildings, manufacturing PC components and managing PC construction, and it strives for popularization of PC architecture.
The PC Architecture Committee is conducting four projects, one for Certifying the quality of PC components, one for Inspecting PC structures, one for Certifying the qualifications of PC building construction management engineers, and one for Certifying the qualifications of PC components manufacturing management engineers.
The PC components quality certification project was launched in 1989 for the purposes of ensuring the quality of PC components and a competent supply for use in buildings, as well as rationalizing and simplifying the supervision systems of each implementing body.
Establishment of certification standards is deliberated by the PC Components Quality Certification Planning Committee, which is composed of persons with academic expertise or vocational experience and each of the implementing bodies, and the practice of inspections based on these certification standards is entrusted to third party institutions.
The PC Components Quality Certification Committee receives the results of this and holds a general review for discussing whether or not to approve the certification standards, and the Chairman of our association approves a person recognized as suitable by the PC Components Quality Certification Planning Committee.
The concrete design standard strength of PC components for N certification is 60 N/㎟ or less and that for H certification is greater than 60 N/ ㎟ but no more than 120 N/㎟ .
As of March 2017, within Japan 65 plants of 44 companies have earned N certification, and 17 plants of 14 companies have earned H certification. Abroad, as of March 2017, two plants of two companies have earned N certification.
The system for inspecting PC structures was inaugurated in the year 2000 in response to the increased importance of ensuring appropriate structural safety and operability of PC architecture as a result of enactment of the Housing Quality Assurance Act and new regulations on performance under the Building Standards Act.
Under it, the PC Structure Inspection Committee was established, composed of persons with academic expertise or vocational experience, and it has conducted inspections of all kinds of PC building structures.
In the 17 years from fiscal 2000 to 2016, it has completed inspections of a total of 16,716 units in 333 buildings in 149 cases.
As the social landscape changes and R&D proceeds, the system for certifying the qualifications of engineers to supervise PC construction methods has been expanded in the scope of its applications since 1989, when it was limited to the earlier W-PC method suitable for medium-rise housing complexes, to inclusion of high-rise housing complexes with the addition of the R-PC and WRPC methods.
Stationing engineers with broad knowledge who could conduct quality control and supervision of construction under the variety of construction methods involved in all of the PC methods became desirable, so the new system was launched in 2006.
The Planning Committee for Certifying Qualifications of PC Building Construction Management Engineers was established, composed of persons with academic expertise or vocational experience and each of the implementing bodies, and it has been certifying the qualifications of PC building construction management engineers.
To qualify, PC building construction management engineers must have public qualifications (Registered Architect of the First Class, or Building Construction Management Engineer of the First Class) and at least one year of experience at managing PC building construction, after which they must enroll in a course offered by our association and pass a test.
They then can apply for registration, after which they are certified. As of March 2017, 479 technicians have been thus registered and certified.


In the construction industry today, due to proceeds in R&D and changes in the social landscape, precast concrete components have expanded in the scope of their applications from the earlier W-PC construction method to R-PC construction method being used in high-rise housing complexes and precast concrete buildings in general.
Together with this, an even wider range of knowledge in precast components manufacturing management is being sought after, such as an emerging trend whereby concrete being used in precast reinforced concrete is becoming even stronger and higher in quality, and revisions being made to the Architectural Institute of Japan’s JASS 10 Precast Concrete Work.
Our association aims to improve our precast components manufacturing plants by improving the quality of our precast components manufacturing management engineers and establishing their place in society.
Therefore, we have established a system for Certifying the qualifications of PC components manufacturing management engineers, which was launched in fiscal 2017. The Planning Committee for Certifying Qualifications of PC Components Manufacturing Management Engineers, composed of persons with academic expertise or vocational experience and some of the implementing bodies, was established to carry out this system.
To qualify, PC components manufacturing management engineers must have at least two years of experience at managing PC components manufacturing (including experience outside of manufacturing management in factories, such as planning, design, technical guidance, and research related to PC components) within the last 15 years. They must then enroll in a course offered by our association and pass a test, after which they can apply for registration and attain certification.
Together with our association’s system for PC components quality certification, we aim to maintain the performance and quality of even better quality precast components.
The PC Architecture Committee publishes a range of technical papers, as listed below, presenting the results of technological development in PC building design, PC component structure and PC building construction management.



The Standardized Architecture Committee comprises member companies (14 companies as of April 1, 2017) involved in manufacturing, designing, constructing, selling or leasing assembled houses or unit houses.
Given the rapid development and changes of these times, housing needs have steadily diversified. On the basis of its 40-plus years of experience and results, the Standardized Architecture Committee is striving to improve technological development and construction management in order to meet these needs.
Through the construction of standardized buildings, the Standardized Architecture Committee contributes to public projects to ensure the safety and livelihood of victims of natural disaster both in Japan and abroad and is helping ameliorate resource concerns and environmental problems through reuse and recycling, and it aims for the realization of an eco-friendly society..
Our association’s standardized buildings have been adopted for a wide range of uses, such as offices, shops, factories, warehouses, lodging, hospitals, government offices and educational facilities, taking advantage of the merits of structures based on prefab construction methods.


Construction of temporary emergency housing when disaster strikes is one of the services the Standardized Architecture Committee provides.
Our association has entered into agreements with all of Japan’s 47 prefectures regarding construction of temporary emergency housing in times of disaster, and we construct temporary emergency housing through our member companies upon the basis of requests from the governor of each prefecture.
In recent years, we have constructed temporary emergency housing for the victims of natural disasters including the Great Hanshin Earthquake, Mt. Usu eruption, Niigata Chuetsu earthquake, Noto Peninsula earthquake, Niigata Chuetsu offshore earthquake,Great East Japan Earthquake and Kumamoto Earthquake.


The Standardized Architecture Committee aims to ensure the safety of its buildings by applying or following Guidelines and Commentary on Managing the Use of Reused Steel Frame Components (3rd Edition) with regard to reused buildings.
We thereby guarantee their safety while contributing to amelioration of resource constraints and environmental problems.

The Standardized Architecture Committee present “Technical Views on Steel-Frame Prefab Building Structures” as the unified technical opinion of our association.

The Housing Committee comprises 21 prefab housing manufacturers as of August 1, 2017.
Playing a leading role in the industry, it engages in activities with the aim of creating highquality living spaces and residential environments and realizing a rich society full of vitality, through both construction and R&D of industrialized housing.
It also strives to create an axis for joint efforts among the member companies to quickly adapt to government policies and changes in the environment surrounding the housing industry.


The Housing Committee is working on developing advanced housing and its technology, and promoting its spread. In addition, it proactively utilizes various performance evaluation indices, such as housing performance labeling and Building Energy-efficiency Labeling System (BELS), to display advanced performance of industrialized housing in an easy-to-understand manner while also improving performance.

The Housing Committee is striving to provide high-quality new housing, such as the spread of long-term high-quality housing, with a long-term view toward housing stock utilization.
It is promoting the flow of high-quality existing housing through appropriately managed maintenance of existing housing, promoting renovation to maintain and improve its performance quality, and other measures such as certification of inspection engineers.

The Housing Committee promotes initiatives for residential and town planning, such as the Smart Wellness City project and Compact City project, in response to the low birthrates, aging society, and decrease in population and the number of households.
It is also looking at raising the level of housing life through use of sensor technologies such as IoT to move toward optimizing the use of residential information communication technology.

The Housing Committee is making steady progress on its environmental action plan “Eco-Action 2020” for realizing a sustainable society.
Above all, it is aiming for the spread of netzero- energy housing, and at the same time promoting the reduction of CO2 emissions and waste through the housing life cycle. In addition, it is working on efforts in consideration of preservation of biodiversity, such as through promoting sustainable wood sourcing and greening.
Besides actively disseminating information about Japan’s industrialized housing technology, residential environment technology and the activities of Japan Prefabricated Construction Suppliers and Manufacturers Association overseas, the Housing Committee also shares overseas initiatives by member companies with international contributions to residential environment.
The Housing Committee aims to improve the skills of members through various types of workshops and symposiums. To create better housing and an improved living environment, it seeks to communicate with various stakeholders, such as residents, by actively providing appropriate information. It also carries out activities such as facility tours, and reporting on the results of its surveys and research.

1) Holding seminars and symposiums

2) Announcing survey and research results
The Education Committee engages in the following activities with the purpose of improving the quality of member company employees in the fields of sales, production, engineering, construction, after-sales service, reform and others.

In contemporary times, housing business employees require advanced knowledge covering diverse fields from architectural regulations in housing business to financial planning.
To meet these demands of the times, a system for certifying the qualifications of housing business employees as prefab housing coordinators (PHC) was set up in 1989 and training courses and certification exams are being held on a nationwide scale.
As of the end of March 2017, a total of 32,255 qualified persons have been registered.
Educational texts have also been created for the purpose of providing general knowledge on housing, with the latest edition (13th edition) being published in June 2017.


Housing industry CS conventions have a long history, starting from 1976 with the TQC Convention (later renamed the TQM Convention), with a total of 43 being held through fiscal 2016.
In a typical year, examples of CS activities of each member company are announced and timely special lectures are held regarding activities for improving customer satisfaction in different business fields, which contribute greatly to the expansion and improvement of CS activities in each member company.

Courses to improve prefab architecture quality have been held annually in Tokyo and other localities starting from 2001.
Persons in charge of practical business and leaders active on the front lines of each field from production, design of individually contracted residences and construction to after-sales service and reform learn the basics of quality control.
Through the exchange of information among the members and research on examples of problems in each field on the basis of the theme chosen each year, the courses contribute greatly to improvement in their qualifications.
From 1994, the Education Committee has been conducting questionnaire surveys of clients centering around the performance of sales reps.
Questionnaires are mailed to 1,300 clients who have purchased newly built homes from the ten prefab housing manufacturers among the member companies and lived in them for an average of one year, and their responses are received.
Based on the results of these surveys, our association works to improve the prefab coordinator system and raise the level of the business managers’ performance.
On the basis of the Act on Assurance of Performance of Specified Housing Defect Warranty (Housing Defect Warranty Fulfillment Act), which took effect on October 1, 2009, any business supplying newly built housing has an obligation to ensure its financial ability to fulfill its responsibilities toward defect warranties by depositing security funds or taking out insurance.
As an “organization supplying housing of high quality,” our association is treated as a specified organization (or approved organization) by the housing defect warranty liability insurance corporations (five companies) specified by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, and when our member companies take out insurance to ensure their financial ability, a committee has been set up to promote defect warranty insurance for the purpose of appropriate planning and management of measures that must be taken.
When our member companies and their affiliated companies apply for group insurance through the offices of our organization, they can receive a discount ※1 on insurance premiums compared to applying for general housing insurance.
※1: For details on the group insurance discount and discount rates, enquire with our association.
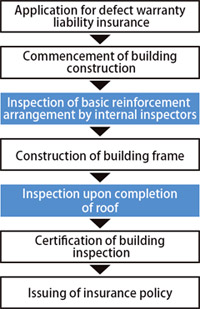
When applying for general housing insurance, two on-site inspections conducted by insurance corporations are necessary (when arranging basic reinforcement and upon completion of roof), but when applying for group insurance, it is possible to have the basic reinforcement arrangement inspection done by group inspectors from one’s own company whose qualifications have been certified by the group.※2
Having one’s own company’s group inspectors conduct the basic r e i n f o r c e m e n t a r r a n g e m e n t inspection provides reduced fees for t h e f i r s t i n s p e c t i o n a n d t h e possibility of smoother progress management because schedule adjustment for inspectors from insurance inspector organizations becomes unnecessary.
※2: There are some cases in which group inspection is not possible. In addition, onsite inspections are not required if the housing comes with housing performance evaluation at construction.

KOJIMACHI NK BLDG., 2-14 2-CHOME, KOJIMACHI,CHIYODA-KU, TOKYO 102-0083 JAPAN
TEL +81-3-5280-3121
FAX +81-3-5280-3127
HOKKAIDO Branch
8-1, HIGASHI SAPPORO 2JO 6CHOME, SHIROISHI-KU,
SAPPORO-CITY, HOKKAIDO 003-8558 JAPAN
TEL +81-11-822-1111
CHUBU Branch
SHOWA BLDG., 3-26 4CHOME, SAKAE, NAKA-KU,
NAGOYA-CITY,AICHI 460-0008 JAPAN
TEL +81-52-251-2488
FAX +81-52-261-4861
KANSAI Branch
INFINI TENMABASHI BLDG., 1-3-5 TANIMACHI,
TENMABASHI, CYUO-KU, OSAKA-CITY, OSAKA 540-0012 JAPAN
TEL +81-6-6943-5016
FAX +81-6-6943-5904
KYUSHU Branch
IWASAKI BLDG., 12-25 NISHINAKASU, CHUO-KU,
FUKUOKA-CITY, FUKUOKA 810-0002 JAPAN
TEL +81-92-716-3930
FAX +81-92-716-3931

